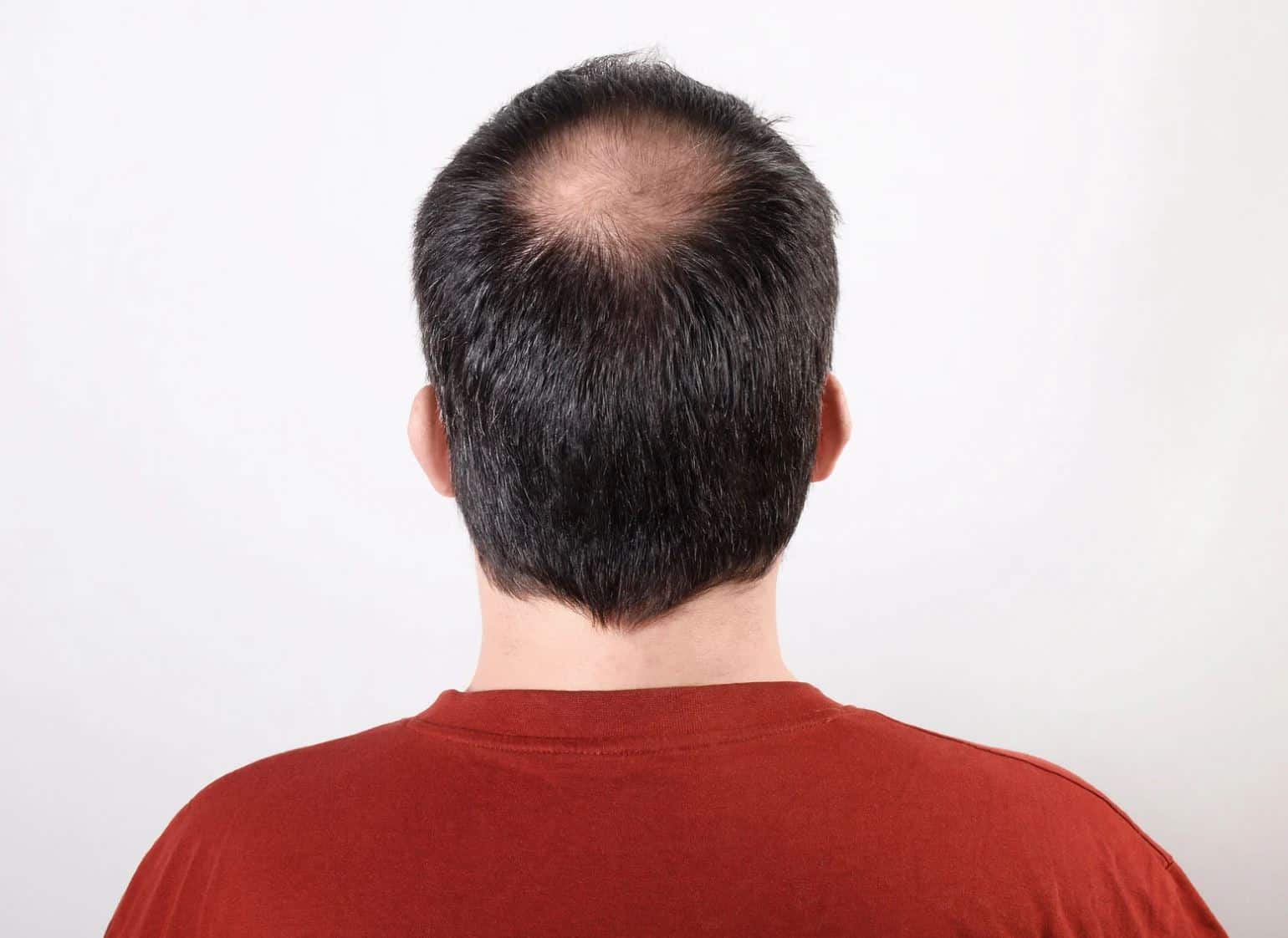
Pattern hair loss or androgenetic alopecia can be treated with the right medications. If you’re experiencing thinning or shedding, FDA-approved medical therapy for hair loss can help slow it down and even regrow hair. Oral and topical medical hair therapy counteracts the follicle-shrinking effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
If you’re losing hair, you’re not out of options. Shapiro Medical offers clinically proven prescription hair loss medications for managing ongoing hair loss and encouraging hair regrowth. To find out which medication is right for you, book a consultation with our hair loss specialists. Here’s what works and why.
1. Propecia (Finasteride)
How It Works
Propecia is one of the most effective medications for treating male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting 5-alpha reductase, an enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the primary hormone responsible for hair follicle miniaturization and hair loss in men.
By reducing DHT levels in the scalp by up to 60-70%, Propecia helps slow down hair loss, prevent further thinning, and in some cases, stimulate regrowth in areas where follicles are still active. Unlike some topical treatments that target symptoms, Propecia directly addresses the hormonal cause of male pattern baldness.
Clinical studies show that 90% of men taking Propecia either maintain their existing hair or experience noticeable regrowth. The drug is most effective for hair loss at the crown and mid-scalp, but it may also help slow recession at the hairline.
Who Should Use Propecia?
- Men with male pattern baldness.
- Men looking to prevent further hair loss and potentially regrow hair.
- Those who prefer an oral medication over a topical solution like minoxidil.
Who Should NOT Use Propecia?
- Women—especially pregnant or breastfeeding women, as finasteride can cause birth defects.
- Men with low testosterone or existing sexual dysfunction. Propecia may worsen symptoms in some cases.
- Anyone who isn’t committed to long-term use. If you stop taking Propecia, hair loss resumes within a few months.
2. Avodart (Dutasteride)
How It Works
Avodart is a DHT-blocking medication similar to Propecia, but more potent. It was originally developed to treat enlarged prostates (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH), but researchers found it also significantly reduces hair loss in men with male pattern baldness.
Like Propecia, Avodart inhibits 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT—the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles and causing hair loss. However, Avodart is more potent because it blocks both types of 5-alpha reductase enzymes (Type I and Type II), whereas Propecia only blocks Type II. This means Avodart lowers DHT levels by over 90%, compared to around 60-70% with Propecia.
Who Should Use Avodart?
- Men with male pattern baldness who need a more potent DHT blocker.
- Men who didn’t see results with Propecia.
- Those with advanced hair loss looking for better preservation of existing hair.
Who Should NOT Use Avodart?
- Women—Avodard is NOT FDA-approved for female hair loss and unsafe during pregnancy.
- Men concerned about potential long-term side effects
- Anyone not willing to commit to ongoing treatment
3. Rogaine (Minoxidil)
How It Works
Rogaine is an FDA-approved topical treatment for hair loss that works by stimulating hair follicles and improving blood flow to the scalp. Unlike Propecia or Avodard, which block DHT to prevent hair loss, Rogaine doesn’t target hormones. Instead, it extends the growth phase of hair follicles, helping to thicken existing hair and promote regrowth.
Minoxidil is available in 2% and 5% strengths, with the 5% version being more effective. It comes in a foam or liquid solution that’s applied directly to the scalp once or twice daily. It works best for thinning hair at the crown and vertex (top of the scalp).
Studies show that 40-60% of users experience noticeable hair regrowth within 3 to 6 months. It’s also common practice to Rogaine with finasteride or dutasteride for a multi-approach treatment.
Who Should Use Rogaine?
- Men and women with early to moderate hair loss.
- Those who prefer a non-prescription, over-the-counter treatment.
- Anyone looking to stimulate regrowth and thicken existing hair.
- Ideal for people using Propecia or Avodard who want additional hair growth support.
Who Should NOT Use Rogaine?
- Men with completely bald areas
- People with scalp conditions or sensitivity
- Anyone not willing to commit long-term
When to Consider a Hair Transplant
If medications like Propecia, Avodart, or Rogaine aren’t giving you the results you want, or if your hair loss is too advanced for them to work effectively, a hair transplant may be the best option.
A hair transplant is the only proven permanent solution for hair loss. Transplanted hair follicles are taken from DHT-resistant areas (typically the back and sides of the head) and implanted into thinning or balding areas. These hairs retain their resistance to hair loss and continue to grow naturally for life.
For natural-looking hair transplants with no visible scars, contact Shapiro Medical Group. We serve patients in and around Minneapolis, including Golden Valley, Columbia Heights, Roseville, Richfield, and the greater Minnesota area.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many men use hair therapy medication?
Millions of men use hair loss medications. Finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) are among the most widely used, with over 2 million prescriptions for finasteride in the U.S. alone.
What is the best treatment for hair loss?
The best treatment depends on the cause and severity of hair loss. Finasteride and minoxidil are the most effective FDA-approved options for male pattern baldness. For severe cases, a hair transplant offers a permanent solution.
What is the medical solution for hair loss?
Medical treatments include DHT blockers (finasteride, dutasteride), growth stimulants (minoxidil), PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy, and low-level laser therapy (LLLT). It’s best to consult a hair loss specialist to know which option is best for you.
Which tablet is best for hair growth?
Finasteride is the most effective oral tablet for preventing hair loss by blocking DHT. Dutasteride (Avodart) is stronger but used off-label.
What drug is approved for hair loss?
The only FDA-approved drugs for hair loss are finasteride and minoxidil. Dutasteride is also used off-label with promising results. Finasteride requires a prescription so consulting a hair loss doctor is required.
When is it too late to use minoxidil?
Minoxidil works best when hair follicles are still active. If a bald area has been hairless for years, minoxidil won’t revive dead follicles. It’s too late when the scalp is completely smooth with no visible thinning hairs.