WHAT IS FUT HAIR TRANSPLANT?
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also called the strip method, is a hair transplant technique used to treat hair loss in both men and women. It is effective for hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), receding hairlines, alopecia areata, and sports injuries.
In FUT procedures, a thin strip of scalp is taken from the donor area (typically from the back of the scalp) and then meticulously divided into individual grafts under a high-powered microscope. These grafts are strategically placed within micro-incisions in a way that mimics natural hair growth patterns.
While FUT initially referred to any procedure producing 1- to 3-hair grafts, it now specifically means the strip harvesting technique. When we mention FUT here, we are referring to follicular unit “strip” surgery.
For the past 25 years, FUT remains the most dependable technique for achieving naturalness and maximum density in the recipient area. Typically, the linear scar resulting from the strip incision is exceptionally fine and often unnoticeable, even when the hair is trimmed as short as 1 cm in length. Many patients opt for this method because it has a long track record of consistently yielding a high number of grafts with exceptional survival rates.
While both FUE and FUT can produce excellent results, some cases require a higher number of grafts to address various types of hair loss, such as general hair thinning, female and male pattern baldness, and receding hairlines.
In these situations, a combination of FUT and FUE techniques is used to obtain more grafts than either method can achieve alone. Additionally, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) treatment can be included to enhance the overall results.
HOW FUT HAIR TRANSPLANT IS DONE
Meeting a patient’s expectations of both naturalness and density are the two most important goals in hair restoration surgery. The strip FUT procedure involves four main steps: 1) donor harvesting, 2) graft preparation, 3) recipient site creation, and 4) graft placement. Every step is an important part of the process that ensures a successful hair transplant.
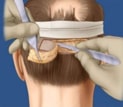
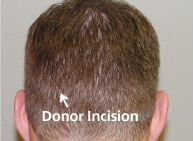
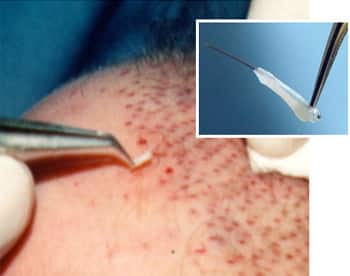
STEP 1: DONOR HARVESTING
The initial phase of the procedure involves delicately removing the donor strip from the recipient site. This is done carefully to minimize damage to the donor hairs and reduce scarring in the donor area after stitching.
The process begins with identifying the safe donor area, which comprises hair that is resistant to hair loss. Before removing the strip, the hair at the site is carefully trimmed. At Shapiro Medical Group, we do this for several important reasons:
- Maintains alignment with the hair’s natural angle during incision.
- Facilitates graft handling during placement.
- Provides a clearer preview of the transplant’s progress, aiding in fine-tuning for optimal results.
Choosing Safe Donor Area
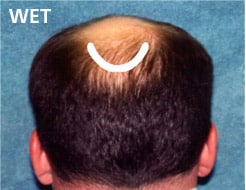
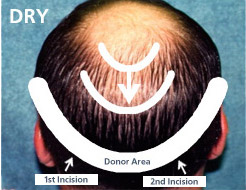
Leave Donor Hair Long
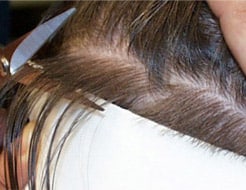
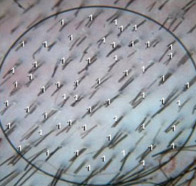
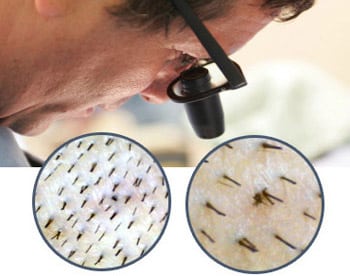
Before extraction, the physician assesses donor area density using digital technology and specialized software, alongside evaluating scalp laxity to determine the safe amount of tissue to remove without causing tension or scarring.
Patients are also instructed to perform scalp stretching exercises beforehand to maximize laxity. Additionally, we administer Vitrase medication to enhance scalp laxity and minimize scarring risk.
Check Donor Laxity
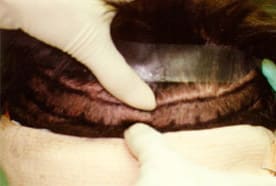
Measure Donor Density

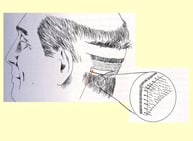
Utilizing 5.0 power surgical loops magnifies the tissue removal area, enabling precise alignment with hair angles to prevent damage. Following strip removal, the donor site is meticulously sutured with a trichophytic closure technique, which promotes scar camouflage by allowing hair growth through the scar tissue.

STEP 2: GRAFT PREPARATION
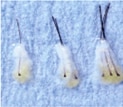
The first step in graft preparation is to sliver the donor tissue under a microscope into thin sections only 1 to 2 hairs wide. With the use of a high-powered microscope, the tissue can be converted into these thin slivers with almost no trauma or transection.
Next, the slivers are cut down into the individual 1- to 4-hair follicular unit grafts and trimmed of as much excess tissue as safely possible. This trimming creates the smallest possible graft that enables the physician to use the smallest possible incision, resulting in less trauma and better graft survival.
During this time, the grafts must remain hydrated and cooled. At SMG, we use a special holding solution called Hypothermosol that has antioxidants, buffers and nutrients to help maximize survival at cooler temperatures.
Donor Strip is Cut into “Thin Slivers” with a Microscope
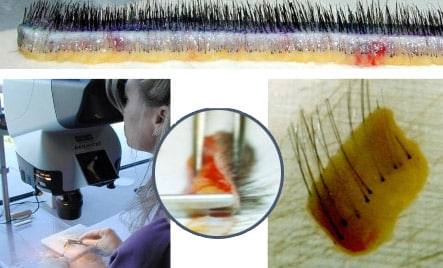

The first step in graft preparation is to sliver the donor tissue under a microscope into thin sections only 1 to 2 hairs wide. With the use of a high-powered microscope, the tissue can be converted into these thin slivers with almost no trauma or transection. Next, the slivers are cut down into the individual 1- to 4-hair follicular unit grafts and trimmed of as much excess tissue as safely possible. This trimming creates the smallest possible graft that enables the physician to use the smallest possible incision, resulting in less trauma and better graft survival. During this time, the grafts must remain hydrated and cooled. At SMG, we use a special holding solution called Hypothermasol that has antioxidants, buffers and nutrients to help maximize survival at cooler temperatures.
STEP 3: RECIPIENT SITE CREATION
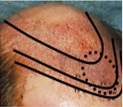
While the grafts are being prepared, the physician will create the recipient sites by first planning the best pattern and distribution of grafts. This plan is created by evaluating the patient’s donor supply, balding area and expectations.
The physician then makes thousands of tiny incisions in a way that will ensure maximum survival of the grafts, minimal trauma to pre-existing hair, and the proper exit angle and direction of the grafts. At SMG, a number of tools are used to accomplish this goal:
- Custom-cut blades that can be matched perfectly to the size of the graft.
- Separation of the 1- to 4-hair grafts so they can be selectively distributed to create more specific density, gradients and natural patterns. The 1-hair grafts are placed in the front for naturalness, and the 3-hair grafts in the center for density.
- True Surgical Loop Magnification to find the space between existing hairs.
- Following the natural angle and direction of hair to mimic natural patterns.
- Both coronal (lateral) or sagittal incisions, depending on the characteristics of each patient.
- Incision densities ranging from 25 to 50+.
- Sessions ranging from as small as 500 (e.g. eyebrows) to as large as 4,500.
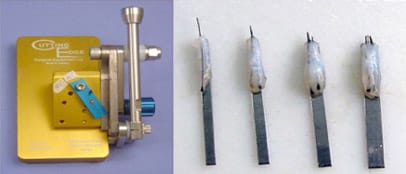
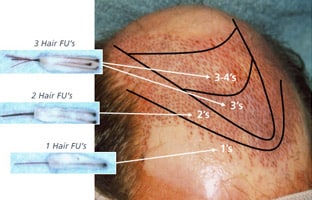
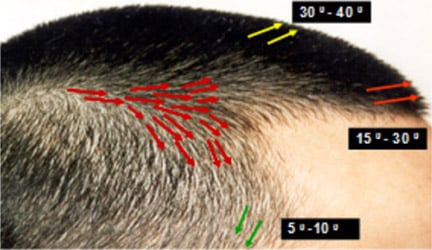
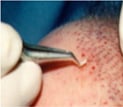
STEP 4: GRAFTS PLACEMENT
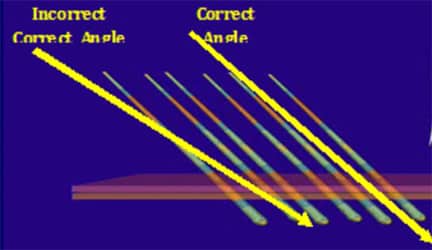
Incorrect placement may result in trauma and reduced graft survival rates. Several methods aid in the placement process:
- Utilization of true surgical magnification to enhance visibility of the recipient sites.
- Use of fingertip cups to securely hold the grafts during placement, preventing dehydration.
- Application of specialized forceps designed for precise graft placement.
- Employing the technique of ‘gentle placement’ to ensure minimal trauma during graft insertion
FUT RECOVERY
Recovery after FUT surgery takes some time, but most people can return to work and normal activities within a week or two. Here’s a general timeline of what you can expect after your FUT procedure:
Recovery after FUT surgery takes some time, but most people can return to work and normal activities within a week or two. Here’s a general timeline of what you can expect after your FUT procedure:
Days 1-3
In the first few days after surgery, your scalp might be swollen and uncomfortable. This is normal. Your surgeon will likely give you pain medication to help. Follow their instructions on how to care for your scalp and any bandages. Try to rest and avoid strenuous activities to help your healing.
Days 5-7
Around this time, your surgeon will likely remove your stitches. You might see scabs on your scalp, and they could itch. It’s important not to scratch or pick at them to avoid damaging the new hair follicles. Keep your scalp clean according to your surgeon’s advice.
Weeks 2-4
During this period, some of the transplanted hair might fall out. This is called “shock loss” and it’s normal. The hair follicles are just resting before they start to grow new hair. Be patient; this is temporary. Keep following your surgeon’s aftercare instructions.
4 Months and Beyond
Around four or five months after the surgery, you should start seeing new hair growth. At first, it might be thin, but it will get thicker over time. Over the next year, you’ll see a big improvement in your hair’s density and appearance.
Regular check-ups with your surgeon will help track your progress and address any concerns. Your surgeon might also suggest hair care products or treatments to support healthy hair growth such as prescriptions treatments, laser therapy, and PRP.
FUT ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES OF STRIP FUT
- Maximized Hair Density: Strip FUT has a proven track record of over 25 years, consistently delivering superior density and coverage.
- Higher Graft Yield: Over a patient’s lifetime, strip FUT typically yields a larger number of grafts compared to exclusive FUE procedures.
- Better Graft Survival: FUT grafts often exhibit slightly better survival rates due to their fuller structure with more protective tissue. Nonetheless, advancements in FUE techniques, such as the Hybrid Blunt Punch and Oscillation System, have led to the production of grafts similar in size to those obtained through FUT.
DISADVANTAGES OF STRIP FUT
- Linear Scar: Unlike FUE, which extracts individual hair follicles, FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the back of the head and using the hair follicles from that strip as grafts. This process leaves a linear scar.
- Longer Healing Time: FUT can take longer to heal compared to FUE due to the larger incision.
- Scar Visibility: While most FUT scars are minimal and inconspicuous, they can be more noticeable if you have very short hair.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
How long does the FUT procedure take?
An FUT hair transplant surgery usually takes between 4 to 10 hours, depending on the number of grafts. The procedure is lengthy because each follicular unit must be carefully separated from the scalp strip.
Am I a good candidate for FUT?
FUT is a suitable option for individuals experiencing pattern baldness, those with adequate donor hair density at the back of the scalp, realistic expectations about results, and good overall health. Conversely, you might not be an ideal candidate if you have very tight scalp skin, a history of poor wound healing or keloid scarring.
We recommend consulting a qualified hair transplant surgeon to determine if FUT is the right procedure for you. The surgeon will assess your scalp health, hair loss pattern, and overall suitability for the surgery.
What are the potential risks of FUT hair transplants?
As with any surgical procedure, FUT comes with potential risks, including infection, bleeding, scarring, follicle damage leading to poor hair growth, numbness in the donor area, and an unnatural-looking hairline if improperly performed. Be sure to discuss these risks thoroughly with your surgeon and don’t hesitate to ask questions before undergoing the procedure.
Are FUT hair transplants permanent?
Yes. The transplanted hair follicles in an FUT hair transplant are genetically resistant to balding and will continue to grow throughout your life. However, it is important to note that the surrounding non-transplanted hair can still thin or fall out over time.
How much does a FUT hair transplant cost?
The cost of an FUT hair transplant can vary widely, depending on your surgeon’s experience and location, the number of grafts transplanted, and the location of the clinic. Some clinics may offer package deals that include medications and follow-up appointments.
If you’re contemplating getting a hair transplant in the Minneapolis area, consider scheduling a consultation at Shapiro Medical Group.
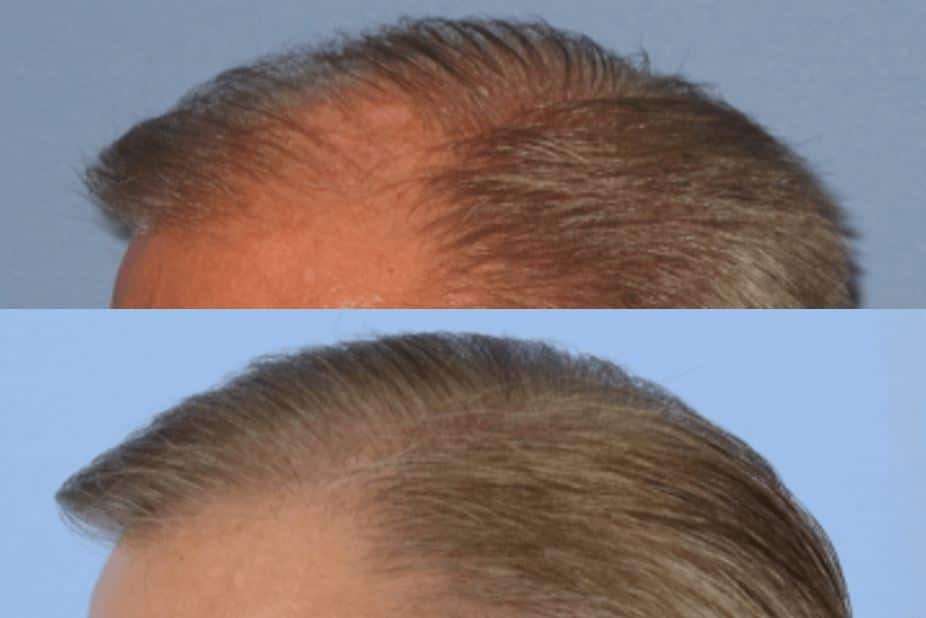
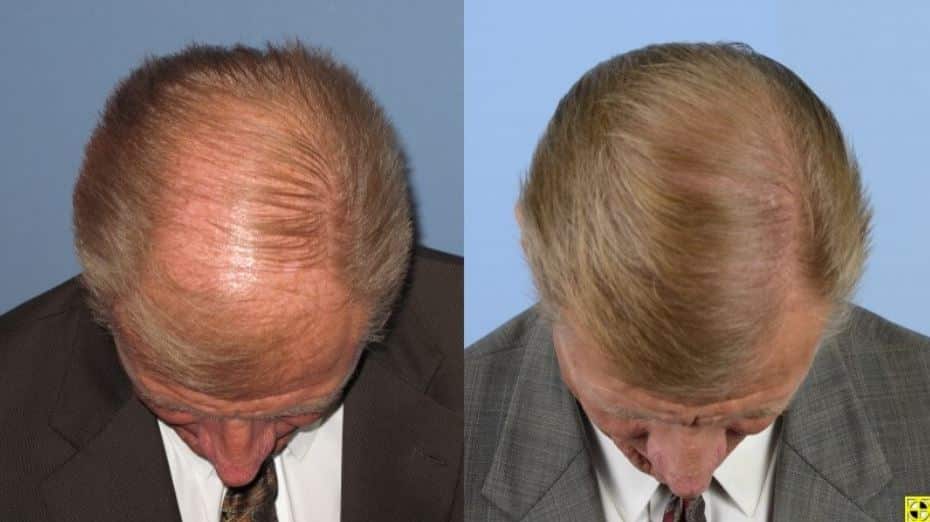
FUT BEFORE AND AFTER PHOTOS
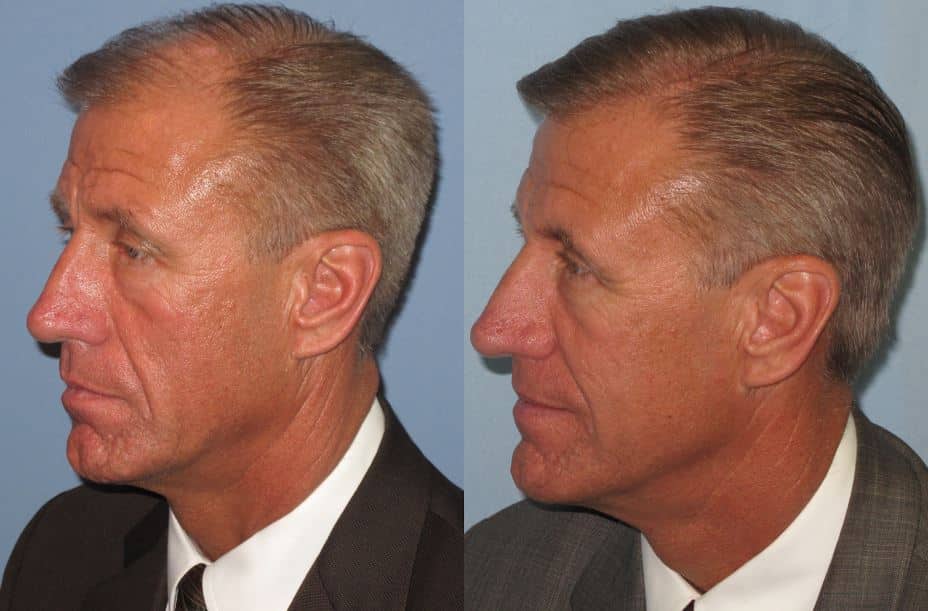
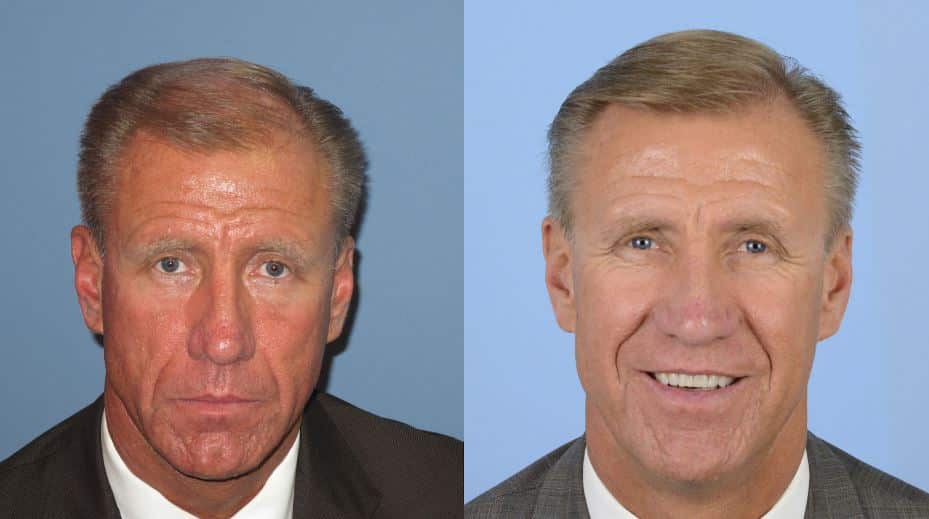
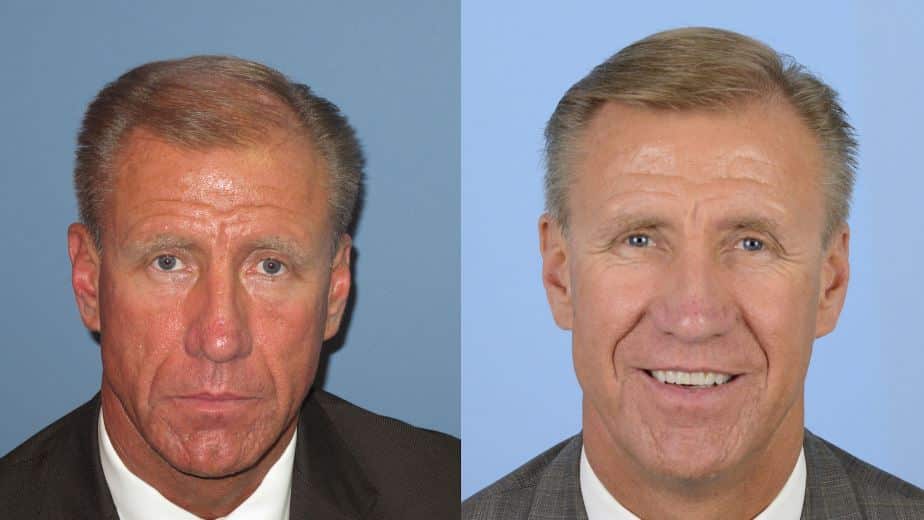



SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
If you’ve tried different hair treatments and products without success, Shapiro Medical Group’s FUT hair transplant can help. FUT offers a permanent solution to hair loss with maximum coverage and natural-looking results.
Dr. Shapiro and his team have helped countless men and women to regrow a full head of hair and regain their confidence. Take control of your hair loss and schedule a consultation with Shapiro Medical Group today.
Shapiro Medical Group is located at 5270 West 84th St., Suite 500 Bloomington, MN 55437. We serve patients in and around Minneapolis, including Minnesota, St. Paul, Bloomington, Eden Prairie, Edina, Minnetonka, Maple Grove, and Plymouth.

